Free Pre Assessment Test for Language Arts Middle School
Welcome to the GACE Heart Grades Language Arts practice test and prep page. We'll exist introducing you lot to the core domains and concepts you need to know to pass the GACE Heart Grades Language Arts test. This is one of the free resource we provide so yous can meet the high-level concepts you will find on the test to guess how much you know.
Quick Links to Help You Navigate This Page
- GACE Middle Grades Linguistic communication Arts Test Data
- Reading
- Writing, Speaking, and Listening
- Language Use and Vocabulary
- Analysis
GACE Middle Grades Language Arts Test Information
The purpose of the GACE Middle Grades Language Arts test is to measure the basic cognition of a prospective educator and their ability to apply principles. This assessment is for anyone wanting to teach language arts in middle schools (grades iv-eight) in Georgia.
Format:
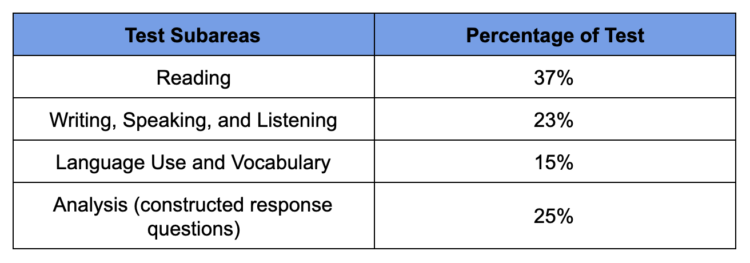
The GACE middle grades language arts assessments is a computer-based test that includes xc selected-response questions and 2 synthetic-response questions. The testing fourth dimension for this assessment is two hours. You will accept an additional 30 minutes for tutorials. The test is broken up into the iv sub-areas listed below.
Toll:
The exam is $123 to be paid past credit or debit card, PayPal, or echeck.
Scoring:
Due to the constructed response questions, scoring results will not be immediately afterward the test is taken. You will exist notified by email when your score report is available. The passing score for the GACE middle grades language arts assessments is 220-249 for the consecration level and 250 for the professional level. Passing at either ane of these levels meets the requirements established by the state of Georgia to laissez passer the content knowledge cess.
Pass rate:
A survey consisting of 603 examinees between 2014-2017 revealed a total of 506 participants passing, making the pass rate percent of 94%.
Written report time:
The amount of fourth dimension you will demand to spend preparing for the
GACE Center Grades Language Arts exam depends upon your existing content cognition.
Ane way to determine your bent for the GACE Middle Grades Language Arts exam is to utilise 240Tutoring materials and practice questions to gauge your understanding of the contents of the exam. Which concepts practice you lot struggle with the most?
Afterward identifying your areas of need, y'all tin can utilise 240Tutoring tools to strengthen your noesis of these concepts until you're gear up for the big day! Remember, it's all-time to spend some time studying each solar day instead of cramming for the exam shortly before you accept it. That fashion, yous'll retain what you learn and you'll too have less stress during the exam.
What examination takers wish they'd known:
- Information technology's a keen strategy to track your time while taking the
test. You can monitor your time past periodically checking the timer in the upper right-manus corner of your screen.
- Test-takers tend to overestimate their abilities to perform well on GACE assessments. Many students regret non putting more time and endeavor into preparing for GACE assessments beforehand. Fortunately, it's like shooting fish in a barrel to avoid this fault by using test grooming materials early. If yous're reading this, you're already starting off on the right human foot!
- Because time management is crucial, skip questions that you find extremely hard and move forward to questions that yous notice easier to answer. Don't worry, you can mark the questions you skip as you take the examination. Try to stop the other questions with x to 15 minutes remaining and utilize that extra time to return to the more challenging questions. If you are unsure of an respond, it is better to guess than to leave a question blank.
- When answering the selected-response questions, you should read all possible answers before mark the correct i. You wouldn't want to miss out on the all-time reply past not reading all of the responses!
- Y'all'll feel more confident if you check out GACE's free guide to taking computerized tests.
Information obtained from ETS.
GACE Middle Grades Language Arts Key Concepts
The Reading subarea has most 33 selected-response questions. These questions account for 37% of the entire exam.
This subarea tin be neatly divided into 3 objectives:
- Literature
- Informational Text
- Comprehension
So, let's talk about the Literature objective get-go.
Literature
This section tests your noesis of literature.
Let'due south talk almost some concepts that you volition more than likely see on the test.
Literary Genres
Characteristics of Poetry
- Written in lines and stanzas
- Some follow the strict length of stanzas and the number of lines
- Well-nigh have figurative language: simile, metaphor, hyperbole, ingemination, etc.
Characteristics of Literary Nonfiction
- Written like fiction, merely includes real people, settings, and plots
- Examples include: autobiography, biography, and essays
Characteristics of Drama
- Similar to a short story, but written strictly with dialogue
- Includes characters, setting, plot, dialogue, theme, and stage directions
Characteristics of Myth
- The story virtually how characters undergo a sequence of events
- Tales that are usually believed as true
- Contains actress-human, inhuman, or heroic characters
Characteristics of Legend
- Stories that were told orally
- The master character is often heroic
- The principal grapheme is a homo, not a god
Characteristics of Fable
- Moral tales usually with animal characters
- Typically curt with no more than 2 or three characters
- Unremarkably, teach a lesson
Theme
The author develops the theme through the plot, characters, and setting. He/she builds the story so the reader has a sure state of mind, ultimately revealing a turning point or low bespeak for one of the characters. Having the graphic symbol larn a lesson or figure something out about themselves at this bespeak portrays the desired theme. A universal theme is one that applies to any reader, no matter their cultural differences or geographic location. Below is a list of common universal themes.
- Hero's Journey
- Stories with characters destined for greatness or unlikely heroes who achieve greatness despite the odds
- Coming of Age
- Generally constitute in children's and young developed books
- Unremarkably includes a young grapheme that deals with the loss of innocence and/or a major change in mindset
- Good v. Evil
- Common in fantasy series
- Explores boxing between good and evil, where skilful usually wins
- Individual five. Society
- Revolves around a character that is an outsider
- Normally, struggle to fit in or rebel confronting society'southward expectations
- Prejudice
- Characters that overcome their prejudices and alter their way of thinking or what destructive consequences prejudice can have
Word Choice
An author uses precise words to create a vivid movie in the reader's mind in guild to accomplish their intended audience. Using a diverseness of word choice creates the meaning and tone the author intended.
- Types of Figurative Language
- Similes, metaphors, and allusions get beyond literal meanings to give readers new insights
- Alliteration, onomatopoeia, and imagery appeal to the reader's senses
- Connotative Language
- Emotions and feelings associated with certain words
- Can exist negative or positive to portray the writer'due south meaning
- Examples: "He's such a dog." "She is so pushy." "There'due south no place like home."
- Informal Language
- Creates a friendly tone due to its conversational tone rather than a formal tone
- Examples: contractions, slang, cliches
Informational Text
This section tests your knowledge of the advisory text.
Here are some concepts that are likely to appear on the test:
Supporting Interpretations
Li
teral v. Inferential Interpretations
- Literal Interpretations
- What the text describes as happening in the story
- This is the fundamental level of comprehension
- Inferential Interpretations
- Using what the text says to determine what it means (read between the lines)
- This requires the reader to brand inferences as they read
- I.e. the daughter makes a sour face when eating something new, can infer that she doesn't like information technology
Textual show is evidence from the text that supports the ideas, opinions, arguments, and thoughts of the readers. Whether making literal or inferential interpretations textual bear witness must exist present. Some events must have happened in the story in order for the reader to literally translate it, while the reader must apply background noesis and/or personal experience to what they take read to make inferential interpretations.
Organizational Patterns
Mutual organizational patterns, besides known as text structures, are used in informational text to assist the author develop a key idea. There are four main text structures including description, cause and effect, chronology or sequence, compare and contrast, and problem and solution.
- Description
- Text provides details of the characteristics of something
- Clues: adjectives, examples, characteristics
- Cause and Issue
- Text describes and event and the reason for it follows
- Clues: as a result, if/then, because
- Chronological
- Text goes in a sequence or describes procedures
- Clues: history, steps, instructions, transition words
- Compare and Contrast
- Text describes similarities and differences
- Clues: same/different, both/neither, on the other paw
- Trouble and Solution
- Text identifies a trouble and one or more possible solutions
- Clues: problem, solution
Comprehension
This department tests your noesis of comprehension.
Let's look at some concepts that will almost likely pop up on the test.
Instructional Strategies
Activating Prior Cognition
- Borer into a educatee'due south prior cognition in lodge for them to accept something to bring to the table before teaching a lesson is imperative.
- Ways to activate prior knowledge:
- KWL Chart: students write and share what they already know (K), what they desire to know (W), and after reading or exploring a variety of texts they fill out what they learn (L)
- Anticipation Guide: ordinarily fix every bit a list of statements where the students either concord or disagree with large themes or ideas that yous will be roofing in class
- Multimedia: before introducing a new topic, show the students a curt video, presentation, or photo request prompting questions about what they find or know nigh the topic
Modeling Metacognitive Practices
- A method to help students understand the way they learn, modeling how students need to retrieve well-nigh their thinking
- Ways to teach metacognitive practices
- Define the term: relate information technology to the driving of your brain
- Ask students to describe benefits, for case, re-reading a passage can help us understand it, jotting notes before writing can aid us if nosotros get "stuck" when writing just like we think earlier we speak
- Gloat metacognitive practices: when students are using advisable practices, celebrate them
- Examples of metacognition: have students share how they can use metacognitive practices in everyday lives, how their parents utilize them at work
- Model: walk students through trouble-solving, higher-guild thinking issues to model how to recall about their thinking
Active Reading
- Reading something with a determination to understand and evaluate it
- Bank check this out for a long list of strategies to exist an active reader: https://www.mpc.edu/Home/ShowDocument?id=30462
Recollect-Pair-Share
- A strategy where students work together to solve a trouble or respond a question almost an assigned reading
- Showtime students call up individually about the answer to the question
- 2d students share ideas with each other
Comprehension Strategies
Making Predictions: making a guess near what will happen in the futurity, using text prove as back up
- Readers who are making predictions are focused on the text at paw, thinking ahead and refining and revising their predictions which supports their comprehension of the text.
Making Connections: making a personal connection about the reader'southward ain experiences to the text
- Readers tin link what they already know to what they are reading, which activated their prior knowledge and supports their comprehension of the text.
Identifying the Primary Thought and Supporting Ideas: finding the topic sentence of a text and the details that back up that topic
- Readers who can identify the main idea and the relationship betwixt information technology and the supporting details are the basis for reading comprehension.
Summarizing: taking a large option of a text and narrowing it downwards to the main points
- Readers who can make up one's mind the essential ideas and consolidate those ideas must have a strong comprehension level of that text.
And that's some basic info about the Reading subarea.
Writing, Speaking, and Listening
The Writing, Speaking, and Listening subarea has well-nigh 26 selected-response questions. These questions business relationship for 23% of the entire exam.
This subarea can be neatly divided into 3 objectives:
- Characteristics of Writing
- Oral Communication
- Instruction
So, let's talk virtually the Characteristics of Writing objective first.
Characteristics of Writing
This section tests your knowledge of the characteristics of writing.
Permit's talk about a concept that you lot will plausibly see on the examination.
Types of Writing
At that place are three main types of writing, including belligerent, informative or explanatory, and narrative.
- Belligerent- taking a position on an result or topic and supporting that position with research
- The position is articulate and concise inside the thesis argument
- Several reasons to back up the position
- Cite sources used in the correct format
- Informative/Explanatory-purpose is to increment knowledge about a topic
- Provides new noesis
- Explains a process
- Provides explanations of why
- Narrative-telling a story
- Characters
- Setting
- Plot
- Conflict
- Indicate of View
Oral Communication
This section tests your noesis of oral advice.
Hither are some concepts that will well-nigh likely appear on the test:
Speech and Presentation Commitment
Communicating conspicuously is one of the nearly effective skills when presenting. Incorporating verbal and nonverbal cues within the speech keeps the audience engaged and interested in what y'all have to say. Below is a shortlist of how to effectively deliver a presentation.
- Eye Contact: make sure to keep middle contact with the audience especially when making key points
- Speech Speed: talk at a normal pace so the audience can hands understand
- The tone of Vox: use a soft tone of vocalization to attract the audition
- Facial Expression: gentle facial expressions will appeal to the audition
- Manus and Body Gestures: use simply when appropriate
Oral Communication
The setting affects oral communication in a variety of ways. When in front of the whole class a teacher will use a loud "presenter" vocalization, while if in pocket-size groups students and teachers will communicate in a whisper. Setting can also affect a student's condolement level of communication which needs to be taken into consideration.
- Components of Effective One-on-Ane Communication
- Model how the exchange should be: heart contact, torso language, responding
- Reinforce Active Listening- focus on listening to empathize rather than listening to reply
- Ask Open-Concluded Questions- permit students an opportunity to share their understandings and thoughts
- Components of Effective Group Communication
- All components of effective one-on-one communication apply.
- Allow multiple students to share. When request open up-ended questions allow students with different opinions or thoughts to share.
- Heed to all student responses. As a teacher, model how students should listen to others and ask follow-up questions.
- Proper Await Time: when asking students higher-guild thinking permit students to jot down ideas so they take notes to become back to in social club to be prepared for grouping discussion.
Educational activity
This section tests your knowledge of instruction.
These are some concepts that are probable to be included on the test:
Writer's Workshop
Writer's workshop is a educatee-centered framework that focuses on writing frequently for an extended time on topics of educatee's choosing. It works in a unique series that follows an intended club for maximum results. Writer's Workshop begins with a mini-lesson, moved to independent writing, conferring with an experienced writer, and finally sharing what the writer has written.
- Mini-Lesson
- 5-ten minutes
- Based on the needs of the majority of students
- Choose aspect to focus on: usually involves procedures, quality of good writers, or editing skills
- Writing
- xxx-45 minutes
- Writing for extended time on topics of their choosing
- Students working at different stages: drafting, planning, revising, and proofreading
- Conferring
- Happening while students are writing: 30-45 minutes
- The teacher walks effectually the room and checks in with students for a couple of minutes
- Allows opportunity for differentiation
- Get together informal assessments to assist instruction
- Sharing
- ten-20 minutes
- Can share their writing at whatsoever indicate in the process
- Writers learn to give and receive feedback from peers
Assessment
The purpose of assessing reading, writing, speaking, and listening individually allows the teacher to sympathize what the pupil'due south strengths and weaknesses are. Reading and listening are comprehension skills while writing and speaking are production skills. Due to this difference, each one must exist individually tested to determine student success in each skill.
Assessment Methods
- Diagnostic
- Given as a pre-assessment to make up one's mind strengths, weaknesses, and prior knowledge to help guide instruction
- Operation-Based
- Measures student's ability to apply skills or knowledge learned in a unit of study
- Norm-Referenced
- Measures student'south performance compared to the average score on a given assessment
- Criterion-Referenced
- Measures performance against a fixed set of criteria
And that's some bones info almost the Writing, Speaking, and Listening subarea.
Language Use and Vocabulary
The Language Use and Vocabulary subarea has virtually 17 selected-response questions. These questions account for 15% of the entire examination.
This subarea can be neatly divided into 2 objectives:
- Language Use
- Vocabulary
So, allow'southward talk about the Language Use objective beginning.
Linguistic communication Use
This department tests your knowledge of language use.
Let'due south talk about some concepts that you will probable see on the exam.
Verb Tenses
The verb tense tells yous when a person did something or when something has happened. The three primary tenses are the past, present, and hereafter. Gerunds are words formed using verbs but human activity like a noun. They can be difficult to place, but they are always verbs that end in -ing.
- Examples of Verbs (past, present, future)
- walked, walk, will walk (virtually verbs)
- brought, bring, will bring (irregular verbs)
- striking, hit, will hit (verbs that stay the same)
- Examples of Gerunds
- Reading
is relaxing.
- I savor
shopping
with friends.
- Her occupation is
writing
.
- Reading
Sentence Types
Declarative Sentence: this is the about common type of sentence. It is used to make a statement.
- Examples:
I love this flick. I have to go to work on Mon. The cereal is in the closet.
Interrogative Judgement: this type of sentence asks a question.
- Examples:
Where are nosotros watching the movie? When practice you go dorsum to work? Would y'all like some cereal?
Exclamatory Sentence: this is similar to a declarative judgement every bit information technology makes a statement, simply it conveys emotion or excitement. It ends in an exclamation mark.
- Examples:
This is the all-time movie e'er! I can't wait to become dorsum to piece of work! Yous have Lucky Charms!
Imperative Sentence: this type of judgement gives a control or order.
- Examples:
Play that movie. Requite me the appointment over again. Bear witness me the options.
Simple Sentence: has the near basic sentence elements–a discipline, verb, and a complete idea. A simple judgement has one independent clause that can stand alone as a complete sentence.
- Examples:
Joe waited for the train. Mary and Samantha took the bus.
Compound Sentence: has two independent clauses continued with a comma and a analogous conjunction. If no analogous conjunction is used to link two independent clauses, it is referred to as a comma splice (an mistake). (FANBOYS- for, and, nor, but, or, however, then)
- Examples:
Joe waited for the train, but the train was late. Mary and Samantha left on the bus before I arrived, so I did not run into them at the bus station.
- Comma Splice:
Information technology is nearly half-past five, we will miss the train.
Complex Judgement: has one independent clause and one dependent clause. A dependent clause is similar to an contained clause, but information technology lacks the elements to make a complete sentence. The dependent clause begins with a subordinating conjunction.
- Examples:
While we waited at the train station, Joe realized that the train was late. Considering Mary and Samantha arrived at the bus station earlier noon, I did non see them at the station.
Vocabulary
This section tests your knowledge of vocabulary.
Allow'south wait at some concepts that are likely to popular up on the test.
Reference Materials
Some examples of print reference materials that support and right linguistic communication usage are dictionaries, thesauri, and glossaries. Dictionaries can assistance a student determine the verbal give-and-take they need to apply for that judgement. It can help them define words equally they read in order to build their vocabulary. A glossary can also aid in a student's comprehension and improve understanding of the text to incorporate into their own vocabulary. A thesaurus will aid a student choose synonyms to improve their writing.
There are digital resource available as well. All of these impress materials are available in digital class, but there are too apps that students can use to help support and correct language usage. Snap and Read is an app that can be added to any device and volition read whatever text that a student highlights. It tin besides change the Lexile level for the pupil to assistance support their language and vocabulary development. Another app that is useful is a co-author, every bit it assists in existent-time, predicting word choice, translation, and speech recognition. It assists in the usage of proper grammer and predicts time to come words based on the topic of the writing piece.
Various Learners
Below is a list of inquiry-based approaches that back up language acquisition and develop the vocabulary for diverse learners, including English Linguistic communication Learners.
- Multi-Sensory Learning: helping a child learn through more one sense
- Pairing new words with pictures
- Pairing new words with gestures
- More senses activated when learning new vocabulary words allows for better remember
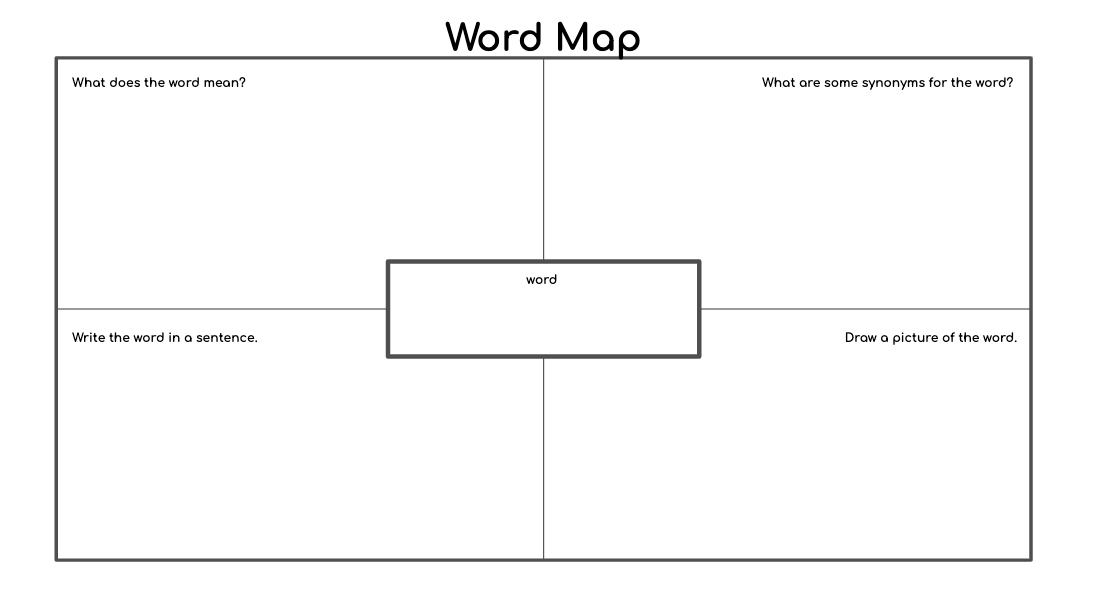
- Graphic Organizers: a visual brandish that represents relationships
- Word Maps: help students develop an understanding of a word by building upon prior knowledge and visually representing new information
- Explicit Instruction: skill-based, simply students are active participants in the learning process
- Four Essential Components of Education Vocabulary according to Michael Graves (2006)
- Providing rich and varied linguistic communication experiences
- Instruction individual words explicitly
- Teaching word-learning strategies
- Fostering Discussion Consciousness
- Four Essential Components of Education Vocabulary according to Michael Graves (2006)
- Modeling: the teacher teaches a new concept or approach to learning while students learn through observation
- Using appropriate vocabulary beyond bookish areas
- Referring to words using correct names (i.east. top number in a fraction: numerator, volume: literature/text)
And that'south some basic info nearly the Language Use and Vocabulary subarea.
Analysis
The Assay subarea has about 28 selected-response questions. These questions account for 25% of the entire exam.
This content category can be neatly divided into 2 sections:
- Literature
- Instruction
Then, permit's talk about the Literature department first.
Literature
This department tests your noesis of literature.
Hither is a concept that is likely to be office of the test:
Literary Elements
Characterization: the creation or construction of a fictional character
- The pace-by-Stride process of how the author introduces and describes a character
- PAIRS: Physical description, Action, Inner thoughts, Reaction, and Speech is how an author develops their characters
Setting: where or when the story takes place
- Initiates the main backdrop and mood of the story
- May include culture, historical time menstruum, and geography
Plot Evolution: a sequence of events within a story
- 5 essential elements: introduction, rising activity, climax, falling action, and resolution
Instruction
This section tests your knowledge of instruction.
Allow'due south talk near some concepts that are likely to be on the examination.
Modeling
Modeled writing is when the teacher is doing all the thinking, talking, and writing. Students are invited to melody in and notice what the writer is doing but practise not offer suggestions on how to better the writing. Instead, students heed and observe while the teacher goes through the writing process making his or her thinking transparent as students find. This type of writing should be washed daily, take nearly five-10 minutes, and occur at the beginning of the writing lesson. Students need to see how a writer thinks in order for them to exist able to produce an age-appropriate piece of writing.
Diversity
Diversity tin be identified by race, gender, and social class, just it as well refers to backgrounds, experiences, and world views. A teacher must have into account all areas of multifariousness to all-time teach their students and be able to understand what students bring to the classroom. Although every student is different, the experience within the classroom should be a safety identify where they can step exterior their condolement zone and engage in their learning. Teachers can incorporate cultural awareness into classroom instruction by taking an involvement in students' backgrounds, maintain high expectations for every pupil, and using a variety of literature.
And that'due south some bones info about the Analysis subarea.
Source: https://www.240tutoring.com/gace-prep/gace-middle-grades-language-arts-assessment-practice-test/
0 Response to "Free Pre Assessment Test for Language Arts Middle School"
Post a Comment